Work on quantum simulations in Nature Physics
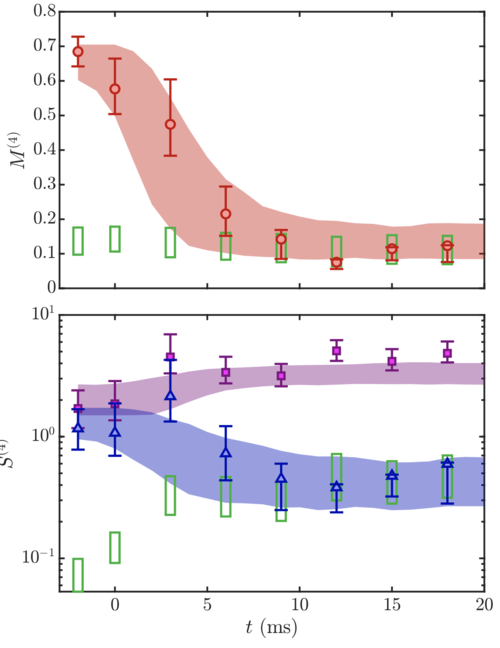
Work on cold atomic quantum simulators probing "Gaussification dynamics" is going to press in Nature Physics. Gaussian models provide an excellent effective description of a plethora of quantum many-body systems ranging from a large variety of condensed matter systems all the way to neutron stars. Gaussian states are common at equilibrium when the interactions are weak. Recently it was proposed that they can also emerge dynamically from a non-Gaussian initial state evolving under non-interacting dynamics. In this work, we present the first experimental observation of such a dynamical emergence of Gaussian correlations in a quantum many-body system. For this, we monitor the connected fourth-order correlations during non-equilibrium dynamics. These dynamics are triggered by abruptly switching off the effective interaction between the collective degrees of freedom that we observe, while leaving the interactions between the microscopic constituents unchanged. Starting from highly non-Gaussian correlations, we observe a Gaussian description becoming increasingly accurate over time. In our closed system with non-interacting effective degrees of freedom, we do not expect full thermalization. This memory of the initial state is confirmed by observing recurrences of non-Gaussian correlations. Our study points to a natural way for Gaussian models to emerge in a wide class of (microscopically interacting) quantum many-body systems.
News from Jan 18, 2021