Work on quantum state tomography in Nature Physics
We identify strong limitations against quantum state tomography of continuous-variable systemssubject to energy constraints inherent in experimental platforms.
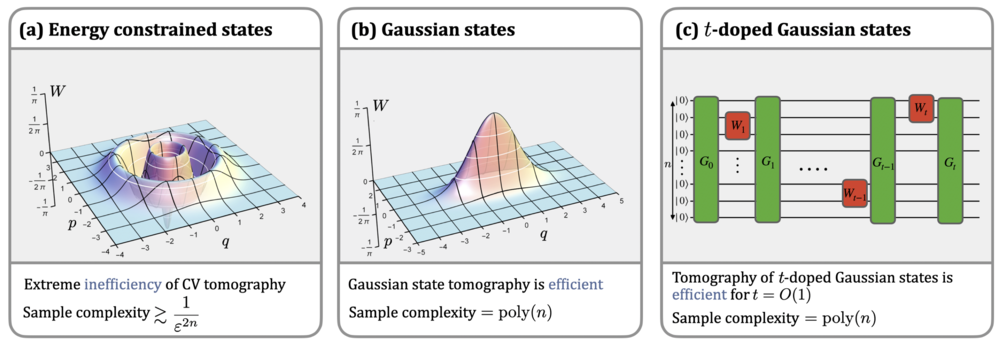
New work published in Nature Physics discusses the striking difficult of continuous variable quantum state tomography: Quantum measurements are probabilistic and, in general, provide only partial information about the underlying quantum state. Obtaining a full classical description of an unknown quantum state requires the analysis of several different measurements, a task known as quantum-state tomography. Here we analyse the ultimate achievable performance in the tomography of continuous-variable systems, such as bosonic and quantum optical systems. We prove that tomography of these systems is extremely inefficient in terms of time resources, much more so than tomography of finite-dimensional systems such as qubits. Not only does the minimum number of state copies needed for tomography scale exponentially with the number of modes, but, even for low-energy states, it also scales unfavourably with the trace-distance error between the original state and its estimated classical description. On a more positive note, we prove that the tomography of Gaussian states is efficient by establishing a bound on the trace-distance error made when approximating a Gaussian state from knowledge of the first and second moments within a specified error bound. Last, we demonstrate that the tomography of non-Gaussian states prepared through Gaussian unitaries and a few local non-Gaussian evolutions is efficient and experimentally feasible.
News from Dec 01, 2025